Have You Tried to Turn It Off and on Again Trump Meme
Donald Trump has been a presidential candidate iii times, in 2000, 2016, and 2020; he also "unofficially" campaigned in 2012 and mulled a run in 2004.[i] His 2nd formal presidential entrada in 2016 was successful; he was elected the 45th president of the Usa on November 8, 2016, and inaugurated on January 20, 2017. He sought reelection in the 2020 United States presidential election, simply lost to Democratic nominee Joe Biden.
Trump's overt political activity started with his publicly suggesting a run for President in the belatedly 1980s. Ever since, Trump has maintained a steady interest in politics, though he was non ever considered a serious candidate. Trump has spoken at the Bourgeois Political Action Briefing (CPAC) multiple times, with his start appearance in 2012. From 2013 to 2015, Trump connected to brand political news headlines but was nonetheless polling depression and non taken seriously by analysts.
Trump would become the 2016 Republican nominee for president of the U.s.a. later on beating sixteen other candidates. The New Yorker said a key cause for Trump's winning of the GOP nominee was that "Despite having demonstrated political cunning in the course of dispatching his sixteen rivals, he has managed to convince many Republican voters that he isn't a politician at all."[2] He became president as a outcome of winning the 2016 presidential election'due south balloter college; it likewise made him the fifth person to be elected president while losing the popular vote. Trump'south presidency saw big levels of cabinet and staff turned over, to an extent unprecedented in modern American history.[iii] He saw numerous allegations of misconduct that resulted in investigations past Congress and Special Quango besides as two impeachments.
On June 18, 2019, Trump announced that he would seek re-election in the 2020 presidential ballot. In September 2020, Trump was nominated for the 2021 Nobel Peace Prize. The election on November 3 was non chosen for either candidate for several days. On November 7, the Associated Printing – along with major TV networks including CNN, ABC News, CBS News, NBC News, and Play a trick on News – called the race for Joe Biden. Trump refused to concede, and the administration did non begin cooperating with president-elect Biden'south transition team until November 23. Trump continues to push the idea that he is the true president of the U.s., which has led to some amount of controversy within the Republican party.
Political activities up to 2015 [edit]
Trump'south political party amalgamation has changed numerous times. He registered every bit a Republican in Manhattan in 1987, switched to the Reform Party in 1999, the Democratic Party in 2001, and back to the Republican Political party in 2009.[4]
Trump first floated the idea of running for president in 1987,[5] placing full-folio advertisements in three major newspapers, proclaiming "America should stop paying to defend countries that can beget to defend themselves."[6] The advertisements besides advocated for "reducing the upkeep arrears, working for peace in Central America, and speeding up nuclear disarmament negotiations with the Soviet Matrimony".[7] DCCC chair Rep. Beryl Anthony Jr. told The New York Times that "the message Trump has been preaching is a Democratic message." Asked whether rumors of a presidential candidacy were truthful, Trump denied being a candidate, but said, "I believe that if I did run for President, I'd win."[7] Co-ordinate to a Gallup poll in December 1988, Trump was the tenth most admired man in America.[viii] [9]
2000 presidential campaign [edit]
In 1999, Trump formed an exploratory commission to seek the nomination of the Reform Party for the 2000 presidential election.[ten] [xi] A July 1999 poll matching him against likely Republican nominee George W. Bush and likely Autonomous nominee Al Gore showed Trump with seven percent support.[12] Trump eventually dropped out of the race, only still went on to win the Reform Party primaries in California and Michigan.[11] [thirteen] After his run, he left the political party due to the interest of David Duke, Pat Buchanan, and Lenora Fulani.[10] He besides considered running for president in 2004.[14] In 2008, subsequently endorsing Democrat Hillary Clinton in the primary, he endorsed Republican John McCain for president in the general ballot.[xv] [16]
2012 presidential speculation [edit]

Trump publicly speculated about running for president in the 2012 ballot, and made his start speaking appearance at the Conservative Political Action Conference (CPAC) in Feb 2011. The speech communication is credited for helping kick-start his political career within the Republican Party.[17]
On May xvi, 2011, Trump announced he would non run for president in the 2012 ballot, putting an cease to what he described every bit "unofficially campaigning".[one] In February 2012, Trump endorsed Manus Romney for president.[18]
Trump'south presidential ambitions were by and large not taken seriously at the time.[19] Trump'south moves were interpreted by some media as possible promotional tools for his reality bear witness The Apprentice.[one] [twenty] [21] Before the 2016 ballot, The New York Times speculated that Trump "accelerated his ferocious efforts to gain stature within the political earth" after Obama lampooned him at the White Firm Correspondents' Association Dinner in April 2011.[22]
In 2011, co-ordinate to Evan Jones, the headmaster of the New York Armed services Academy at the time, the then-superintendent Jeffrey Coverdale had demanded Trump'south academic records, to hand them over to "prominent, wealthy alumni of the school who were Mr. Trump's friends" at their request. Coverdale said he had refused to hand over Trump's records to trustees of the schoolhouse, and instead sealed Trump'southward records on campus. Jones said: "It was the only time in my education career that I ever heard of someone'south record being removed," while Coverdale further said: "Information technology's the only time I ever moved an alumnus's records." The incident reportedly happened days after Trump demanded President Barack Obama'due south academic records.[23]
2013–2015 [edit]
In 2013, Trump spoke at CPAC again;[24] he railed against illegal immigration, bemoaned Obama'due south "unprecedented media protection", advised against harming Medicare, Medicaid, and Social Security, and suggested that the authorities "have" Republic of iraq's oil and utilize the gain to pay a meg dollars each to families of dead soldiers.[25] [26] He spent over $one one thousand thousand that yr to inquiry a possible 2016 candidacy.[27]
In October 2013, New York Republicans circulated a memo suggesting Trump should run for governor of the state in 2014 against Andrew Cuomo. Trump responded that while New York had problems and its taxes were too high, he was not interested in the governorship.[28] A February 2014 Quinnipiac poll had shown Trump losing to the more popular Cuomo by 37 points in a hypothetical election.[29]
2016 presidential entrada [edit]
Republican primaries [edit]

On June 16, 2015, Trump announced his candidacy for President of the United States at Trump Belfry in Manhattan. In the speech, Trump discussed illegal immigration, offshoring of American jobs, the U.South. national debt, and Islamic terrorism, which all remained large priorities during the campaign. He besides appear his campaign slogan: "Brand America Smashing Once again".[30] [31] Trump said his wealth would brand him immune to force per unit area from entrada donors.[32] He declared that he was funding his own entrada,[33] but according to The Atlantic, "Trump's claims of cocky-funding have always been dubious at best and actively misleading at worst."[34]
In the primaries, Trump was one of seventeen candidates for the 2016 Republican nomination. This was, at the time, the largest presidential field in American history.[35] Trump's campaign was initially not taken seriously by political analysts, merely he apace rose to the top of stance polls.[36] The New Yorker attributed Trump's clinching of the Republican nomination largely to the political party base's "general disgust with professional politicians" and Trump's ability to distinguish himself from traditional Republican politicians.[2]
On Super Tuesday, Trump received the virtually votes, and he remained the front end-runner throughout the primaries. By March 2016, Trump was poised to win the Republican nomination.[37] After a landslide win in Indiana on May 3, 2016 – which prompted the remaining candidates Ted Cruz and John Kasich to suspend their presidential campaigns – RNC chairman Reince Priebus declared Trump the presumptive Republican nominee.[38]
Full general election entrada [edit]
After becoming the presumptive Republican nominee, Trump shifted his focus to the general election. Trump began candidature against Hillary Clinton, who became the presumptive Democratic nominee on June half dozen, 2016.
Clinton had established a meaning atomic number 82 over Trump in national polls throughout near of 2016. In early July, Clinton'southward lead narrowed in national polling averages following the FBI's re-opening of its investigation into her ongoing electronic mail controversy.[39] [twoscore] [41]

On July 15, 2016, Trump announced his selection of Indiana governor Mike Pence every bit his running mate.[42] Four days later, the two were officially nominated past the Republican Party at the Republican National Convention.[43] The list of convention speakers and attendees included former presidential nominee Bob Dole, but the other prior nominees did not nourish.[44] [45]
On September 26, 2016, Trump and Clinton faced off in their first presidential debate, which was held at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York.[46] The second presidential debate was held at Washington Academy in St. Louis, Missouri. The beginning of that debate was dominated past references to a recently leaked tape of Trump making sexually explicit comments, which Trump countered by referring to alleged sexual misconduct on the role of Pecker Clinton. Prior to the debate, Trump had invited four women who had accused Bill Clinton of impropriety to a printing conference. The last presidential debate was held on October 19 at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas. Trump'due south refusal to say whether he would accept the result of the election, regardless of the outcome, drew particular attention, with some saying it undermined democracy.[47] [48]
Political positions [edit]
Trump's entrada platform emphasized renegotiating U.S.–China relations and free trade agreements such equally NAFTA and the Trans-Pacific Partnership, strongly enforcing immigration laws, and building a new wall along the U.Due south.–Mexico border. His other campaign positions included pursuing energy independence while opposing climate change regulations such as the Clean Power Programme and the Paris Understanding, modernizing and expediting services for veterans, repealing and replacing the Affordable Care Deed, abolishing Common Core education standards, investing in infrastructure, simplifying the tax lawmaking while reducing taxes for all economic classes, and imposing tariffs on imports past companies that offshore jobs. During the entrada, he as well advocated a largely not-interventionist arroyo to foreign policy while increasing war machine spending, extreme vetting or banning immigrants from Muslim-majority countries[49] to pre-empt domestic Islamic terrorism, and aggressive military action against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. During the campaign Trump repeatedly called NATO "obsolete".[fifty] [51]
His political positions accept been described as populist,[52] [53] [54] and some of his views cross party lines. For example, his economical campaign programme calls for big reductions in income taxes and deregulation,[55] consequent with Republican Party policies, along with meaning infrastructure investment,[56] usually considered a Democratic Party policy.[57] [58] Co-ordinate to political writer Jack Shafer, Trump may be a "fairly conventional American populist when information technology comes to his policy views", merely he attracts costless media attention, sometimes past making outrageous comments.[59] [60]
Trump has supported or leaned toward varying political positions over time.[61] [62] [63] Political leader has described his positions as "eclectic, improvisational and often contradictory",[63] while NBC News counted "141 distinct shifts on 23 major issues" during his campaign.[64]
Campaign rhetoric [edit]
In his campaign, Trump said he disdained political definiteness; he also said the media had intentionally misinterpreted his words, and he made other claims of adverse media bias.[65] [66] [67] In part due to his fame, and due to his willingness to say things other candidates would non, and because a candidate who is gaining footing automatically provides a compelling news story, Trump received an unprecedented amount of free media coverage during his run for the presidency, which elevated his standing in the Republican primaries.[68]
Fact-checking organizations have denounced Trump for making a record number of false statements compared to other candidates.[69] [seventy] [71] At least four major publications – Politico, The Washington Post, The New York Times, and the Los Angeles Times – accept pointed out lies or falsehoods in his campaign statements, with the Los Angeles Times saying that "Never in mod presidential politics has a major candidate fabricated faux statements every bit routinely as Trump has".[72] NPR said Trump's entrada statements were frequently opaque or suggestive.[73]
Trump's penchant for hyperbole is believed to accept roots in the New York existent manor scene, where Trump established his wealth and where puffery abounds.[74] Trump adopted his ghostwriter's phrase "true hyperbole" to depict his public speaking.[74] [75]
Back up from the far right [edit]
According to Michael Barkun, the Trump entrada was remarkable for bringing fringe ideas, beliefs, and organizations into the mainstream.[76] During his presidential campaign, Trump was defendant of pandering to white supremacists.[77] [78] [79] He retweeted open racists,[80] [81] and repeatedly refused to condemn David Duke, the Ku Klux Klan or white supremacists, in an interview on CNN's State of the Matrimony, saying he would first need to "practise enquiry" because he knew nada about Duke or white supremacists.[82] [83] Duke himself enthusiastically supported Trump throughout the 2016 primary and election, and has said he and agreeing people voted for Trump because of his promises to "take our country dorsum".[84] [85]
After repeated questioning by reporters, Trump said he disavowed David Duke and the KKK.[86] Trump said on MSNBC's Morning Joe: "I disavowed him. I disavowed the KKK. Practise you lot desire me to do information technology again for the 12th time? I disavowed him in the past, I disavow him at present."[86]
The alt-right movement coalesced around Trump'due south candidacy,[87] due in part to its opposition to multiculturalism and immigration.[88] [89] [xc] Members of the alt-right enthusiastically supported Trump's campaign.[91] In August 2016, he appointed Steve Bannon – the executive chairman of Breitbart News – as his campaign CEO; Bannon described Breitbart News as "the platform for the alt-right".[92] In an interview days after the election, Trump condemned supporters who celebrated his victory with Nazi salutes.[93] [94]
Financial disclosures [edit]
As a presidential candidate, Trump disclosed details of his companies, avails, and revenue sources to the extent required by the FEC. His 2015 report listed assets above $i.4 billion and outstanding debts of at least $265 million.[95] [96] The 2016 course showed little alter.[97]
Trump has not released his tax returns, contrary to the do of every major candidate since 1976 and breaking his hope in 2014 to release them if he ran for office.[98] He said his tax returns were being audited, and his lawyers had brash him against releasing them.[99] Trump has told the press his tax rate was none of their business, and that he tries to pay "as little revenue enhancement as possible".[100]
In Oct 2016, portions of Trump'southward land filings for 1995 were leaked to a reporter from The New York Times. They show that Trump declared a loss of $916 one thousand thousand that twelvemonth, which could have let him avert taxes for up to 18 years. During the 2d presidential debate, Trump best-selling using the deduction, but declined to provide details such as the specific years it was applied.[101]
On March 14, 2017, the first ii pages of Trump'due south 2005 federal income tax returns were leaked to MSNBC. The document states that Trump had a gross adjusted income of $150 million and paid $38 meg in federal taxes. The White House confirmed the authenticity of the documents.[102] [103]
On April 3, 2019, the House Means and Means Committee made a formal request to the Internal Revenue Service for Trump's personal and business organization taxation returns from 2013 to 2018, setting a deadline of Apr 10.[104] That mean solar day, Treasury secretary Steven Mnuchin said the deadline would not be met,[105] and the borderline was extended to April 23, which also was not honored,[106] and on Mayvi Mnuchin said the request would exist denied.[107] On May 10, 2019, committee chairman Richard Neal subpoenaed the Treasury Department and the IRS for the returns and seven days later the subpoenas were defied.[108] [109] A fall 2018 draft IRS legal memo asserted that Trump must provide his tax returns to Congress unless he invokes executive privilege, contradicting the administration's justification for defying the before subpoena.[110] Mnuchin asserted the memo really addressed a different thing.[111]
Ballot to the presidency [edit]
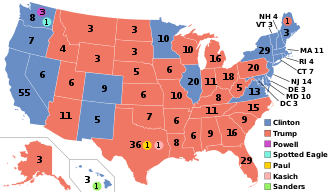
2016 balloter vote results
On November 8, 2016, Trump received 306 pledged electoral votes versus 232 for Clinton. The official counts were 304 and 227 respectively, subsequently defections on both sides.[112] Trump received virtually 2.nine 1000000 fewer popular votes than Clinton, which made him the 5th person to exist elected president while losing the popular vote.[113] [a] Clinton was ahead nationwide with 65,853,514 votes (48.18%) to 62,984,828 votes (46.09%).[116]
Trump's victory was considered a stunning political upset past virtually observers, as polls had consistently showed Hillary Clinton with a nationwide – though diminishing – pb, as well as a favorable advantage in most of the competitive states. Trump's support had been modestly underestimated throughout his entrada,[117] and many observers blamed errors in polls, partially attributed to pollsters overestimating Clinton'due south support among well-educated and nonwhite voters, while underestimating Trump'southward support among white working-grade voters.[118] The polls were relatively accurate,[119] but media outlets and pundits alike showed overconfidence in a Clinton victory despite a large number of undecided voters and a favorable concentration of Trump's core constituencies in competitive states.[120]
Trump won thirty states, including Michigan, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin, which had been considered a blue wall of Democratic strongholds since the 1990s. Clinton won 20 states and the District of Columbia. Trump's victory marked the return of a Republican White House combined with control of both chambers of Congress.
Trump is the wealthiest president in U.S. history, fifty-fifty after adjusting for inflation,[121] and at the time of his inauguration, the oldest person to take part every bit president.[b] [122] He is also the first president who did non serve in the armed forces or hold constituent or appointed government office prior to being elected.[123] [124] [125] Of the 43[c] previous presidents, 38 had held prior constituent office, two had not held elective office but had served in the Cabinet, and 3 had never held public role simply had been commanding generals.[125]
In September 2020, Trump was nominated for the 2021 Nobel Peace Prize. A far-right Norwegian politician nominated Trump'southward name citing his role in the peace bargain between State of israel and the United Arab Emirates.[127]
Presidency [edit]

Trump was unsuccessful in his efforts to repeal the Affordable Intendance Act (ACA) only rescinded the individual mandate and took measures to hinder the ACA'south functioning. Trump sought substantial spending cuts to major welfare programs, including Medicare and Medicaid. He signed the Great American Outdoors Human action, reversed numerous environmental regulations, and withdrew from the Paris Agreement on climatic change. He signed criminal justice reform through the First Step Deed and successfully appointed Neil Gorsuch, Brett Kavanaugh, and Amy Coney Barrett to the Supreme Court. In economic policy, he partially repealed the Dodd–Frank Act and signed the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. He enacted tariffs, triggering retaliatory tariffs from Mainland china, Canada, United mexican states, and the Eu. He withdrew from the Trans-Pacific Partnership negotiations and signed the USMCA, a successor agreement to NAFTA. The federal deficit increased under Trump due to spending increases and revenue enhancement cuts.
He implemented a controversial family separation policy for migrants apprehended at the U.S.–United mexican states border. Trump's demand for the federal funding of a edge wall resulted in the longest U.s.a. government shutdown in history. He deployed federal law enforcement forces in response to the racial unrest in 2020. Trump's "America First" strange policy was characterized by unilateral actions, disregarding traditional allies. The administration implemented a major arms sale to Saudi arabia; denied citizens from several Muslim-majority countries entry into the U.S; recognized Jerusalem every bit the majuscule of Israel; and brokered the Abraham Accords, a serial of normalization agreements between State of israel and various Arab states. His administration withdrew U.Due south. troops from northern Syrian arab republic, allowing Turkey to occupy the surface area. His administration likewise made a conditional deal with the Taliban to withdraw U.Southward. troops from Afghanistan in 2021. Trump met Democratic people's republic of korea'south leader Kim Jong-un three times. Trump withdrew the U.S. from the Iran nuclear understanding and afterwards escalated tensions in the Persian Gulf by ordering the assassination of General Qasem Soleimani.
Robert Mueller's Special Counsel investigation (2017–2019) ended that Russian federation interfered to favor Trump'due south candidacy and that while the prevailing evidence "did not plant that members of the Trump entrada conspired or coordinated with the Russian government," possible obstructions of justice occurred during the course of that investigation.
Trump attempted to pressure level Ukraine to denote investigations into his political rival Joe Biden, triggering his start impeachment by the House of Representatives on December 18, 2019, but he was acquitted past the Senate on February 5, 2020.
Trump reacted slowly to the COVID-19 pandemic, ignored or contradicted many recommendations from health officials in his messaging, and promoted misinformation nearly unproven treatments and the availability of testing.
Post-obit his loss in the 2020 presidential ballot to Biden, Trump refused to concede and initiated an extensive campaign to overturn the results, making imitation claims of widespread electoral fraud. On January 6, 2021, during a rally at The Ellipse, Trump urged his supporters to "fight like hell" and march to the Capitol, where the electoral votes were existence counted past Congress in guild to formalize Biden'southward victory. A mob of Trump supporters stormed the Capitol, suspending the count and causing Vice President Mike Pence and other members of Congress to exist evacuated. On January 13, the Firm voted to impeach Trump an unprecedented second fourth dimension for "incitement of insurrection," but he was afterward acquitted by the Senate again on February 13, later he had already left office. Trump had historically low approval ratings, and scholars and historians rank his presidency as one of the worst in American history.
Protests [edit]

Women's March in Washington on Jan 21, 2017, a twenty-four hour period afterwards the inauguration
Some rallies during the main flavour were accompanied by protests or violence, including attacks on Trump supporters and vice versa both inside and outside the venues.[128] [129] [130] Trump'due south election victory sparked protests across the United states, in opposition to his policies and his inflammatory statements. Trump initially said on Twitter that these were "professional protesters, incited by the media", and were "unfair", but he later tweeted, "Dear the fact that the small groups of protesters last nighttime accept passion for our great country."[131] [132]
In the weeks following Trump's inauguration, massive anti-Trump demonstrations took place, such every bit the Women Marches, which gathered two,600,000 people worldwide,[133] including 500,000 in Washington alone.[134] Marches against his travel ban began beyond the land on January 29, 2017, but 9 days after his inauguration.[135]
2020 presidential campaign [edit]
Trump signaled his intention to run for a second term by filing with the FEC within a few hours of assuming the presidency.[136] This transformed his 2016 election committee into a 2020 reelection 1.[137] Trump marked the official start of the campaign with a rally in Melbourne, Florida, on February xviii, 2017, less than a month subsequently taking office.[138] Past January 2018, Trump's reelection committee had $22 million in manus,[139] and it had raised a total corporeality exceeding $67 million past December 2018.[140] $23 million was spent in the fourth quarter of 2018, as Trump supported various Republican candidates for the 2018 midterm elections.[141]
2020 election loss [edit]

2020 electoral vote results
On November iii, 2020 Trump lost re-ballot to Democratic nominee and former vice president Joe Biden. Trump received 232 balloter votes to Biden's 306. Trump received 74,216,154 in the popular vote to Biden's 81,268,924.
See also [edit]
- Business career of Donald Trump
- Media career of Donald Trump
Notes [edit]
- ^ Records on this matter date from the year 1824. The number "5" includes the elections of 1824, 1876, 1888, 2000, and 2016. Despite their similarities, some of these five elections had peculiar results; e.g. John Quincy Adams trailed in both the national pop vote and the electoral college in 1824 (since no one had a majority in the balloter college, Adams was chosen by the Business firm of Representatives), and Samuel Tilden in 1876 remains the merely losing candidate to win an actual majority of the pop vote (rather than just a plurality).[114] [115]
- ^ Joe Biden became the oldest president to take office in 2021.
- ^ Grover Cleveland was the 22nd and 24th president.[126]
References [edit]
- ^ a b c CNN Political Unit (May sixteen, 2011). "Trump not running for president". CNN . Retrieved May xvi, 2011.
- ^ a b "How Donald Trump Won the G.O.P. Nomination". The New Yorker. May iv, 2016. Retrieved September 24, 2021.
- ^ Tenpas, Kathryn Dunn (Apr thirteen, 2020). "And and then at that place were 10: With 85% turnover beyond President Trump's A Team, who remains?". Brookings Establishment . Retrieved September 24, 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-condition (link) - ^ Gillin, Joshua (August 24, 2015). "Bush-league says Trump was a Democrat longer than a Republican 'in the last decade'". PolitiFact . Retrieved March 18, 2017.
- ^ "For Donald Trump, the 1980s still concord relevance". The Mercury News. January ii, 2017. Retrieved August 29, 2021.
- ^ Oreskes, Michael (September 2, 1987). "Trump Gives a Vague Hint of Candidacy". The New York Times . Retrieved February 17, 2016.
- ^ a b Butterfield, Fox (Feb 12, 1988). "Trump Urged To Caput Gala Of Democrats". The New York Times.
- ^ Kranish & Fisher 2017, p. 3. sfn error: no target: CITEREFKranishFisher2017 (aid)
- ^ Gallup 1990, p. 3. sfn error: no target: CITEREFGallup1990 (help)
- ^ a b Trump, Donald J. (February xix, 2000). "What I Saw at the Revolution". The New York Times.
- ^ a b Winger, Richard (Dec 25, 2011). "Donald Trump Ran For President in 2000 in Several Reform Party Presidential Primaries". Ballot Access News.
- ^ Johnson, Glen. "Donald Trump eyeing a run at the White House". Standard-Speaker. Hazelton, Pennsylvania.
- ^ "CA Secretarial assistant of Land – Principal 2000 – Statewide Totals". ca.gov. Archived from the original on February 16, 2015. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- ^ Travis, Shannon (May 17, 2011). "Was he ever serious? How Trump strung the land along, again". CNN . Retrieved June seven, 2015.
- ^ https://amp.cnn.com/cnn/2016/07/12/politics/donald-trump-hillary-clinton-good-president/alphabetize.html
- ^ "Trump endorses McCain". CNN. September 18, 2008. Retrieved July 12, 2016.
- ^ Belonsky, Andrew (Feb 10, 2011). "GOProud Leads 'Trump in 2012' Movement at CPAC". Towleroad.com.
- ^ "Trump endorses Romney, cites tough China position and electability". Fox News. February two, 2012.
- ^ MacAskill, Ewen (May 16, 2011). "Donald Trump bows out of 2012 US presidential election race". The Guardian.
Few U.S. political commentators took his campaign seriously and many suggested he was only in it for the publicity.
- ^ Grier, Peter (February 10, 2011). "Donald Trump says he might run for president. Three reasons he won't". The Christian Science Monitor . Retrieved April 21, 2011.
- ^ Linkins, Jason (February xi, 2011). "Donald Trump Brings His 'Pretend To Run For President' Act To CPAC". The Huffington Postal service . Retrieved April 21, 2011.
- ^ Haberman, Maggie; Burns, Alexander (March 12, 2016). "Donald Trump's Presidential Run Began in an Endeavor to Gain Stature". The New York Times . Retrieved April 13, 2018.
- ^ Fisher, Marc (March 5, 2019). "'Take hold of that record': How Trump's high school transcript was hidden". The Washington Postal service . Retrieved June 9, 2019.
- ^ Moody, Chris (March 5, 2013). "Donald Trump to address CPAC". Yahoo! News . Retrieved March 6, 2013.
- ^ Madison, Lucy (March 15, 2013). "Trump: Immigration reform a "suicide mission" for GOP". CBS News.
- ^ Amira, Dan (March 15, 2013). "Photos of Donald Trump Delivering His Cocky-Aggrandizing CPAC Speech to a Half-Empty Ballroom". New York (magazine).
- ^ "Trump researching 2016 run". Page Six. May 27, 2013.
- ^ Spector, Joseph (October 14, 2013). "N.Y. Republicans want Donald Trump to run for governor". USA Today . Retrieved October 31, 2013.
- ^ Miller, Jake (Feb 13, 2014). "Trump trumped past Cuomo in N.Y. governor race, poll finds". CBS News . Retrieved February 9, 2017.
- ^ Trump, Donald (June 16, 2015). Hither's Donald Trump'southward Presidential Announcement Speech (Speech). Trump Tower, New York Urban center – via Time. Transcript of total speech
- ^ "Donald Trump Presidential Campaign Announcement Full Speech (C-SPAN)" (Video). YouTube. C-SPAN. June 16, 2015. Retrieved June 2, 2018.
- ^ Lerner, Adam B. (June 16, 2015). "The 10 best lines from Donald Trump's proclamation oral communication". Pol . Retrieved June vii, 2018.
- ^ @realDonaldTrump (September 5, 2015). "Past self-funding my campaign, I am not controlled past my donors, special interests or lobbyists. I am but working for the people of the U.South.!" (Tweet). Retrieved June seven, 2018 – via Twitter.
- ^ Graham, David A. (May xiii, 2016). "The Lie of Trump's 'Self-Funding' Campaign". The Atlantic . Retrieved June vii, 2018.
- ^ Linshi, Jack (July 7, 2015). "More People Are Running for Presidential Nomination Than Ever". Time . Retrieved February 14, 2016.
- ^ Reeve, Elspeth (Oct 27, 2015). "How Donald Trump Evolved From a Joke to an Nigh Serious Candidate". The New Republic . Retrieved July 23, 2018.
- ^ Bump, Philip (March 23, 2016). "Why Donald Trump is poised to win the nomination and lose the general election, in 1 poll". The Washington Post.
- ^ Nussbaum, Matthew (May 3, 2016). "RNC Chairman: Trump is our nominee". Politico . Retrieved May four, 2016.
- ^ Hartig, Hannah; Lapinski, John; Psyllos, Stephanie (July 19, 2016). "Poll: Clinton and Trump At present Tied as GOP Convention Kicks Off". NBC News.
- ^ "2016 Full general Ballot: Trump vs. Clinton". The Huffington Post . Retrieved October 3, 2016.
- ^ "General Ballot: Trump vs. Clinton". RealClearPolitics . Retrieved October 3, 2016.
- ^ Levingston, Ivan (July 15, 2016). "Donald Trump officially names Mike Pence for VP". CNBC.
- ^ "Trump closes the deal, becomes Republican nominee for president". Fox News. July 19, 2016.
- ^ Timm, Jane C. (July 17, 2016). "9 Elephants in the Room at RNC: Who's Missing From the Speakers List". NBC News . Retrieved Baronial 16, 2016.
- ^ Raju, Manu (May 5, 2016). "Flake, McCain split over bankroll Trump". CNN . Retrieved May seven, 2016.
- ^ "2016 Presidential Fence Schedule". September 23, 2015. Retrieved September 30, 2016.
- ^ "U.s.a. presidential fence: Trump won't commit to accept ballot issue". BBC News. October 20, 2016. Retrieved October 27, 2016.
- ^ "How Us media reacted to the tertiary presidential debate". Australian Dissemination Corporation. October 20, 2016. Retrieved October 27, 2016.
- ^ "Trump's promises earlier and after election". BBC Online. September 19, 2017.
- ^ Johnson, Jenna (April 12, 2017). "Trump on NATO: 'I said it was obsolete. Information technology's no longer obsolete.'". The Washington Mail service . Retrieved November 26, 2019.
- ^ Edwards, Jason A. (2018). "Make America Great Again: Donald Trump and Redefining the U.S. Role in the World". Communication Quarterly. 66 (ii): 176. doi:10.1080/01463373.2018.1438485. ISSN 0146-3373. S2CID 149040989.
On the entrada trail, Trump repeatedly called North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) 'obsolete'
- ^ Muller, Jan-Werner (2016). What Is Populism?. Academy of Pennsylvania Press. p. 101. ISBN978-0-8122-9378-4.
- ^ Kazin, Michael (March 22, 2016). "How Tin Donald Trump and Bernie Sanders Both Exist 'Populist'?". The New York Times Magazine.
- ^ Becker, Bernie (Feb xiii, 2016). "Trump'south half-dozen populist positions". Political leader.
- ^ "Tax Reform". Donald J. Trump for president website. Archived from the original on January iv, 2016. Retrieved January 6, 2016.
- ^ Ehrenfreund, Max (December sixteen, 2015). "Liberals will dearest something Donald Trump said final night". The Washington Post.
- ^ Sharman, Jon (Dec 21, 2016). "Democrats tin can finally agree with Donald Trump on something". The Independent . Retrieved December 21, 2016.
- ^ Williams, Mason B. (January 7, 2017). "Would Trump'due south Infrastructure Program Gear up America's Cities?". The Atlantic.
- ^ Shafer, Jack (May 2016). "Did We Create Trump?". Politico.
... Trump's outrageous comments about John McCain, Muslims, the 14th Amendment and all the remainder ...
- ^ Trump & Schwartz 2009, p. 56. sfn error: no target: CITEREFTrumpSchwartz2009 (help)
- ^ Fahrenthold, David A. (August 17, 2015). "20 times Donald Trump has changed his listen since June". The Washington Post.
- ^ Hensch, Mark (July 12, 2015). "'Meet the Press' tracks Trump's flip-flops". The Colina.
- ^ a b Noah, Timothy (July 26, 2015). "Will the real Donald Trump please stand up upwardly?". Politico.
- ^ Timm, Jane C. "A Total List of Donald Trump's Rapidly Changing Policy Positions". NBC News . Retrieved July 12, 2016.
- ^ Walsh, Kenneth T. (August 15, 2016). "Trump: Media Is 'Dishonest and Corrupt'". U.Southward. News & Globe Written report.
'If the disgusting and corrupt media covered me honestly and didn't put false meaning into the words I say, I would exist chirapsia Hillary past xx percentage,' Trump likewise tweeted Dominicus.
- ^ Koppel, Ted (July 24, 2016). "Trump: "I feel I'm an honest person"". CBS News.
Well, I recollect that I'm an honest person... I feel I'1000 an honest person. And I don't listen being criticized at all past the media, but I do wanna – y'all know, I do want them to be direct virtually it.
- ^ Blake, Aaron (July 6, 2015). "Donald Trump is waging war on political correctness. And he's losing". The Washington Post.
- ^ Cillizza, Chris (June 14, 2016). "This Harvard report is a powerful indictment of the media'due south part in Donald Trump's ascent". The Washington Mail service.
- ^ "The 'King of Whoppers': Donald Trump". FactCheck.org. Dec 21, 2015.
- ^ Holan, Angie Drobnic; Qiu, Linda (December 21, 2015). "2015 Lie of the Year: the campaign misstatements of Donald Trump". PolitiFact.
- ^ Farhi, Paul (February 26, 2016). "Think Trump's incorrect? Fact checkers can tell you lot how ofttimes. (Hint: A lot.)". The Washington Post.
- ^ Stelter, Brian (September 26, 2016). "The weekend America's newspapers chosen Donald Trump a liar". CNN.
- ^ McCammon, Sarah (August x, 2016). "Donald Trump'due south controversial speech oft walks the line". NPR.
Many of Trump'southward opaque statements seem to rely on proposition and allusion.
- ^ a b Flitter, Emily; Oliphant, James (August 28, 2015). "All-time president always! How Trump's dear of hyperbole could backlash". Reuters.
- ^ Konnikova, Maria (Jan 20, 2017). "Trump's Lies vs. Your Encephalon". Politico . Retrieved March 31, 2018.
- ^ Barkun, Michael (2017). "President Trump and the Fringe". Terrorism and Political Violence. 29 (3): 437. doi:10.1080/09546553.2017.1313649. ISSN 1556-1836. S2CID 152199771.
- ^ Lopez, German language (August xiv, 2017). "We need to stop acting similar Trump isn't pandering to white supremacists". Vox . Retrieved January two, 2018.
- ^ Blow, Charles M. (September 18, 2017). "Is Trump a White Supremacist?". The New York Times.
- ^ Kharakh, Ben; Primack, Dan (March 22, 2016). "Donald Trump's Social Media Ties to White Supremacists". Fortune.
- ^ White, Daniel (Jan 26, 2016). "Trump Criticized for Retweeting Racist Business relationship". Time.
- ^ "White Nationalists and the Alt-Correct Gloat Trump's Victory". Southern Poverty Law Heart. November 9, 2016. Retrieved November x, 2016.
- ^ Chan, Melissa (February 28, 2016). "Donald Trump Refuses to Condemn KKK, Disavow David Duke Endorsement". Time . Retrieved Jan 20, 2018.
- ^ Lozada, Carlos (December 30, 2016). "Donald Trump and the alt-right: A marriage of convenience". The Washington Post . Retrieved March 18, 2017.
- ^ Nelson, Libby (August 12, 2017). ""Why we voted for Donald Trump": David Knuckles explains the white supremacist Charlottesville protests". Vox . Retrieved August 18, 2018.
- ^ Cummings, William (August 15, 2017). "Former KKK leader David Knuckles praises Trump for his 'courage'". USA Today . Retrieved August 18, 2018.
- ^ a b Scott, Eugene (March iii, 2016). "Trump denounces David Duke, KKK". CNN.
- ^ Ohlheiser, Abby (June three, 2016). "Anti-Semitic Trump supporters made a giant list of people to target with a racist meme". The Washington Post.
- ^ Weigel, David (Baronial 20, 2016). "'Racialists' are cheered by Trump's latest strategy". The Washington Post . Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Krieg, Gregory (August 25, 2016). "Clinton is attacking the 'Alt-Right' – What is it?". CNN . Retrieved Baronial 25, 2016.
- ^ Sevastopulo, Demetri. "'Alt-right' move makes mark on U.s. presidential election". Financial Times.
- ^ Hawley, George (2017). Making Sense of the Alt-Right. Columbia Academy Press. ISBN978-0-231-54600-3.
- ^ Wilson, Jason (November 15, 2016). "Clickbait scoops and an engaged alt-right: everything to know nigh Breitbart News". The Guardian . Retrieved Nov 18, 2016.
- ^ "Trump disavows 'alt-correct' supporters". BBC Online. November 23, 2016.
- ^ "Donald Trump'southward New York Times Interview: Full Transcript". The New York Times. Nov 23, 2016.
- ^ "Donald Trump wealth details released by federal regulators". Yahoo! News. July 22, 2015. Archived from the original on Baronial 1, 2015. Retrieved August 9, 2015.
- ^ "Executive Branch Personnel Public Fiscal Disclosure Report (U.South. OGE Form 278e)" (PDF). U.Due south. Function of Regime Ethics. July 15, 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 23, 2015 – via Bloomberg Businessweek.
- ^ Alesci, Cristina; Frankel, Laurie; Sahadi, Jeanne (May 19, 2016). "A peek at Donald Trump's finances". CNN. Retrieved May 20, 2016.
- ^ Rappeport, Alan (May 11, 2016). "Donald Trump Breaks With Recent History by Not Releasing Taxation Returns". The New York Times . Retrieved July 19, 2016.
- ^ Isidore, Chris; Sahadi, Jeanne (February 26, 2016). "Trump says he can't release revenue enhancement returns because of audits". CNN . Retrieved February 26, 2016.
- ^ Kopan, Tal (May xiii, 2016). "Trump on his tax rate: 'None of your business organization'". CNN.
- ^ Eder, Steve; Twohey, Megan (October 10, 2016). "Donald Trump Acknowledges Not Paying Federal Income Taxes for Years". The New York Times.
- ^ Bakery, Peter; Drucker, Jesse; Craig, Susanne; Barstow, David (March 15, 2017). "Trump Wrote Off $100 Million in Business Losses in 2005". The New York Times . Retrieved March 15, 2017.
- ^ Jagoda, Naomi. "WH releases Trump tax info ahead of MSNBC report: He paid $38M in federal taxes in '05". The Hill . Retrieved March 15, 2017.
- ^ Gordon, Marcy (April 4, 2019). "House chairman asks IRS for 6 years of Trump's tax returns". AP News.
- ^ Stein, Jeff; Paletta, Damian (Apr x, 2019). "Treasury says it will miss Democrats' deadline for turning over Trump tax returns, casts skepticism over request". The Washington Post.
- ^ Lorenzo, Aaron (April 23, 2019). "IRS blows deadline to hand over Trump revenue enhancement returns". Pol.
- ^ Rappeport, Alan (May vi, 2019). "Steven Mnuchin Refuses to Release Trump'south Tax Documents to Congress". The New York Times.
- ^ Fandos, Nicholas (May x, 2019). "Business firm Ways and Means Chairman Subpoenas Trump Tax Records". The New York Times.
- ^ Rubin, Richard (May 17, 2019). "Mnuchin Defies Subpoena for President Trump'due south Revenue enhancement Returns". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Stein, Jeff; Dawsey, Josh (May 21, 2019). "Confidential draft IRS memo says tax returns must be given to Congress unless president invokes executive privilege". The Washington Post.
- ^ Eckert, Toby (May 22, 2019). "Mnuchin dismisses IRS memo saying Congress must be given Trump's revenue enhancement returns". Politico.
- ^ Schmidt, Kiersten; Andrews, Wilson (December 19, 2016). "A Celebrated Number of Electors Defected, and Most Were Supposed to Vote for Clinton". The New York Times . Retrieved Jan 31, 2017.
- ^ Desilver, Drew (December twenty, 2017). "Trump's victory another example of how Electoral College wins are bigger than popular vote ones". Pew Research Centre.
- ^ Thomas, G. Scott (2015). Counting the Votes: A New Way to Clarify America's Presidential Elections. ABC-CLIO. p. 125. ISBN978-1-4408-3883-5.
- ^ Cheney, Kyle (December 14, 2016). "Trump lawyer cites 1876 crunch to rebuke Electoral College suit". Political leader.
- ^ "Official 2016 Presidential General Election Results" (PDF). Federal Election Commission. Dec 2017. Retrieved February 12, 2018.
- ^ Tani, Maxwell (November 9, 2016). "Trump pulls off biggest upset in U.S. history". Politico . Retrieved Nov 9, 2016.
- ^ Cohn, Nate (November nine, 2016). "Why Trump Won: Working-Class Whites". The New York Times . Retrieved November ix, 2016.
- ^ Silver, Nate (January 17, 2017). "Can Yous Trust Trump's Blessing Rating Polls?". FiveThirtyEight.
- ^ Argent, Nate (September 21, 2017). "The Media Has A Probability Problem". FiveThirtyEight.
- ^ Martin, Emmie (January 23, 2017). "Donald Trump is officially the richest United states president in history". Business Insider . Retrieved September 9, 2017.
- ^ Kurtzlebel, Danielle (June fourteen, 2016). "It's Trump'south Birthday. If He Wins, He'd Be The Oldest President Ever To Have Office". NPR . Retrieved May iii, 2019.
- ^ Weber, Peter (November 9, 2016). "Donald Trump volition be the first U.S. president with no government or armed services experience". The Week.
- ^ Yomtov, Jesse (Nov 8, 2016). "Where Trump ranks amidst to the lowest degree experienced presidents". U.s. Today.
- ^ a b Crockett, Zachary (Nov 11, 2016). "Donald Trump will exist the only US president ever with no political or armed services feel". Phonation . Retrieved January 3, 2017.
- ^ "Will Trump Exist The 44th Or 45th President? Yes And Yes". NPR. November x, 2016. Archived from the original on February seven, 2017. Retrieved June four, 2017.
- ^ "Trump Nobel Peace Prize nomination - what you need to know". BBC . Retrieved September 9, 2020.
- ^ Moyer, Justin Wm.; Starrs, Jenny; Larimer, Sarah (March eleven, 2016). "Trump supporter charged after sucker-punching protester at Northward Carolina rally". The Washington Mail service . Retrieved August 31, 2016.
- ^ Sullivan, Sean; Miller, Michael Due east. (June 3, 2016). "Ugly, bloody scenes in San Jose as protesters attack Trump supporters outside rally". The Washington Post . Retrieved August 31, 2016.
- ^ Diamond, Jeremy (May 28, 2016). "Pro-Trump, anti-Trump groups clash in San Diego". CNN . Retrieved August 31, 2016.
- ^ Cummings, William (November 11, 2016). "Trump calls protests 'unfair' in first controversial tweet as president-elect". Us Today . Retrieved November 27, 2016.
- ^ Colson, Thomas (November eleven, 2016). "Trump says protesters have 'passion for our dandy country' afterward calling demonstrations 'very unfair'". Business concern Insider . Retrieved Nov fourteen, 2016.
- ^ Przybyla, Heidi Yard.; Schouten, Fredreka (January 22, 2017). "At 2.6 million strong, Women'southward Marches crush expectations". USA Today (online ed.). Retrieved Jan 22, 2017.
- ^ Buncombe, Andrew (January 22, 2017). "We asked ten people why they felt empowered wearing a pink 'pussy' lid". The Contained . Retrieved January xv, 2017.
- ^ Varkiani, Adrienne Mahsa (Jan 28, 2017). "Here's your list of all the protests happening against the Muslim Ban". ThinkProgress . Retrieved September 18, 2018.
- ^ Westwood, Sarah (January 22, 2017). "Trump hints at re-ballot bid, vowing 'eight years' of 'great things'". The Washington Examiner . Retrieved Feb 19, 2017.
- ^ Morehouse, Lee (January 31, 2017). "Trump breaks precedent, files equally candidate for re-ballot on first twenty-four hour period". Phoenix, Arizona: KTVK. Archived from the original on Feb 2, 2017. Retrieved Feb 19, 2017.
- ^ Graham, David A. (February 15, 2017). "Trump Kicks Off His 2020 Reelection Campaign on Sabbatum". The Atlantic . Retrieved February 19, 2017.
- ^ McCormick, John; Jacobs, Jennifer (January 31, 2018). "Trump'southward 2020 Re-Ballot Committee Has $22.1 Million in the Bank". Bloomberg News . Retrieved March 24, 2018.
- ^ "Donald J. Trump for President, Inc. / Presidential – Main campaign commission / Fiscal summary". Federal Ballot Commission. Dec 31, 2018. Retrieved Feb 5, 2019.
- ^ Donald J. Trump for President, Inc. (January 31, 2019). "FEC Form 3P – Report of receipts and disbursements – Filing FEC-1312481". Federal Ballot Commission . Retrieved February v, 2019.
External links [edit]
- President Trump'south profile on WhiteHouse.gov
- Archive of Donald Trump'southward Tweets
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Political_career_of_Donald_Trump
0 Response to "Have You Tried to Turn It Off and on Again Trump Meme"
Post a Comment